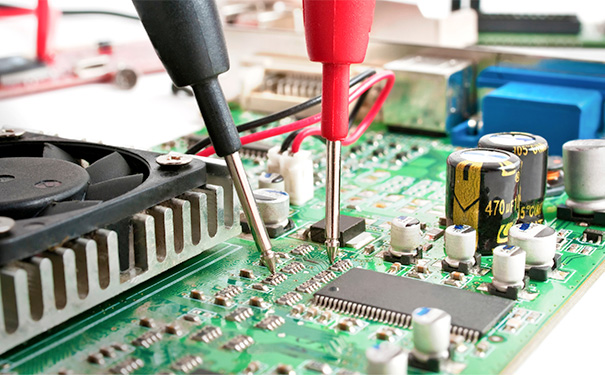
The process flow of PCBA patch processing is very complex, including many important processes such as PCB board manufacturing process, component procurement and inspection, SMT patch assembly, DIP plug-in, and PCBA testing. PCBA functional testing refers to a test method that provides a simulated operating environment for the test target board to work in various design states, so as to obtain the parameters of each state to verify the function of the PCBA. Simply put, it is to load a suitable stimulus on the PCBA and measure whether the response of the output terminal meets the requirements. Generally refers to the PCBA function test after the installed circuit board is powered on.
PCBA functional test content Measurement of functional parameters such as voltage, current, power, power factor, frequency, duty cycle, and position determination. The functional test of PCBA contains the content: General part:
1: Power supply part test - whether the power supply works normally, test the voltage of each point - use a comparator or other
2: Port (interface) test, whether there is Short&Open, resulting in an exception
3: Integrated circuit module IC I/O read and write function test - Flash&EEPROM&CPU&SDRAM&Logic IC etc
4: Special function test (different circuit board requirements are inconsistent) - such as with infrared, an external receiver is required
PCBA functional testing involves analog, digital, memory, RF, and power circuits, often using different test strategies. Testing includes a number of practically significant functional paths and structural verification (determining that there are no hardware bugs) to make up for the missing parts of the previous testing process. This requires continuously applying a large number of analog/digital stimuli to the PCBA, while monitoring the same number of analog/digital responses and having complete control over their execution. There are many forms of PCBA functional test systems and equipment, each of which has advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, time, effectiveness and maintainability.
PCBA functional test equipment
Model test system
Theoretically the easiest way to test the functionality of a device (board or module) is to place it in a model system or subsystem that behaves like a real environment and see if it works. If it is normal, we can have a high degree of confidence that it is good, if not, the technician will test it in the hope of finding out the cause of the failure to guide the repair. In practice, however, this plug-in power-up method has many disadvantages and is rarely effective, although it can sometimes be used as a complement to other test scenarios.
Test Bench
A test bench is a conventional test environment, including stimulus/response interfaces to the device under test, test sequences and controls specified by special test procedures. Excitation and response are typically provided by standard power supplies and experimental instruments, specialized switches, loads, and end-custom electronics such as digital excitation. The fixture is a very important part here, providing the correct signal path and connectivity to the device under test. In many cases, fixtures are basically custom-made for each application, requiring a combination of manual settings to set up. The testing process and control are usually carried out manually, sometimes with the assistance of a PC, and are prescribed by written protocols or procedures. The test bench is connected to a specific product, which has the advantages of relatively low cost and simple equipment, but less flexibility when dealing with multiple products.
Dedicated test equipment
In theory, dedicated test equipment is a system that automates the operation of the test bench. The heart of the system is usually a computer, which is controlled through a dedicated bus and some programmable instruments. Speed, performance, availability, cost, and other factors influence the choice of instrument bus and architecture. Various instruments and general purpose equipment are stacked in one or more vertical enclosures and then connected to the device under test. With automation, setup time, test time, and overall operation are faster and easier than manual test benches. STE can be expanded to meet a variety of performance needs and is typically used in production or repair centers. The most obvious of STE is the overall cost: equipment investment cost, operating cost, and program development cost.
Automatic test equipment
General Purpose Automatic Test Equipment (GPATE, or ATE for short) is a very advanced and flexible solution to meet a variety of product and program testing requirements. System integration, signal connectivity flexibility, value-added hardware and software, test-oriented languages, graphical user interface, etc. are the main differences between ATE and STE. In addition to the benefits of full instrument integration, ATE provides better solutions for signal routing and connectivity. ATE-specific backplanes in most cases include an analog bus that allows the instrument to be directly connected to any pin without complicating internal and external wiring. This flexibility is often extended to combine analog and digital channels, allowing users to connect digital or analog stimuli and measure any receiver pin at any time. As a result, not only is the cost greatly simplified, but the test procedure is also easier to implement. According to the different control modes, it can be divided into: manual control PCBA function test, semi-automatic control PCBA function test, fully automatic control PCBA function test. With the rapid development of science and technology, in order to save production costs and improve production efficiency, some of the current PCBA functional tests use fully automatic test solutions. At present, for the PCBA function test of some simple boards under test, based on the consideration of simplifying the design and reducing the manufacturing cost, manual or semi-automatic test solutions are still used.